Trailing behind the exit of the United States, China has taken an interest in the Middle East, brokering diplomatic deals between Saudi Arabia and Iran. This is a surprising role for China to take on, as the country has, in the past, shown relatively little interest in that region of the world. The spike in China’s expressed interest in international affairs has drawn attention from all parts of the world and is making everyone question why now and for what purpose.
China in the Middle East
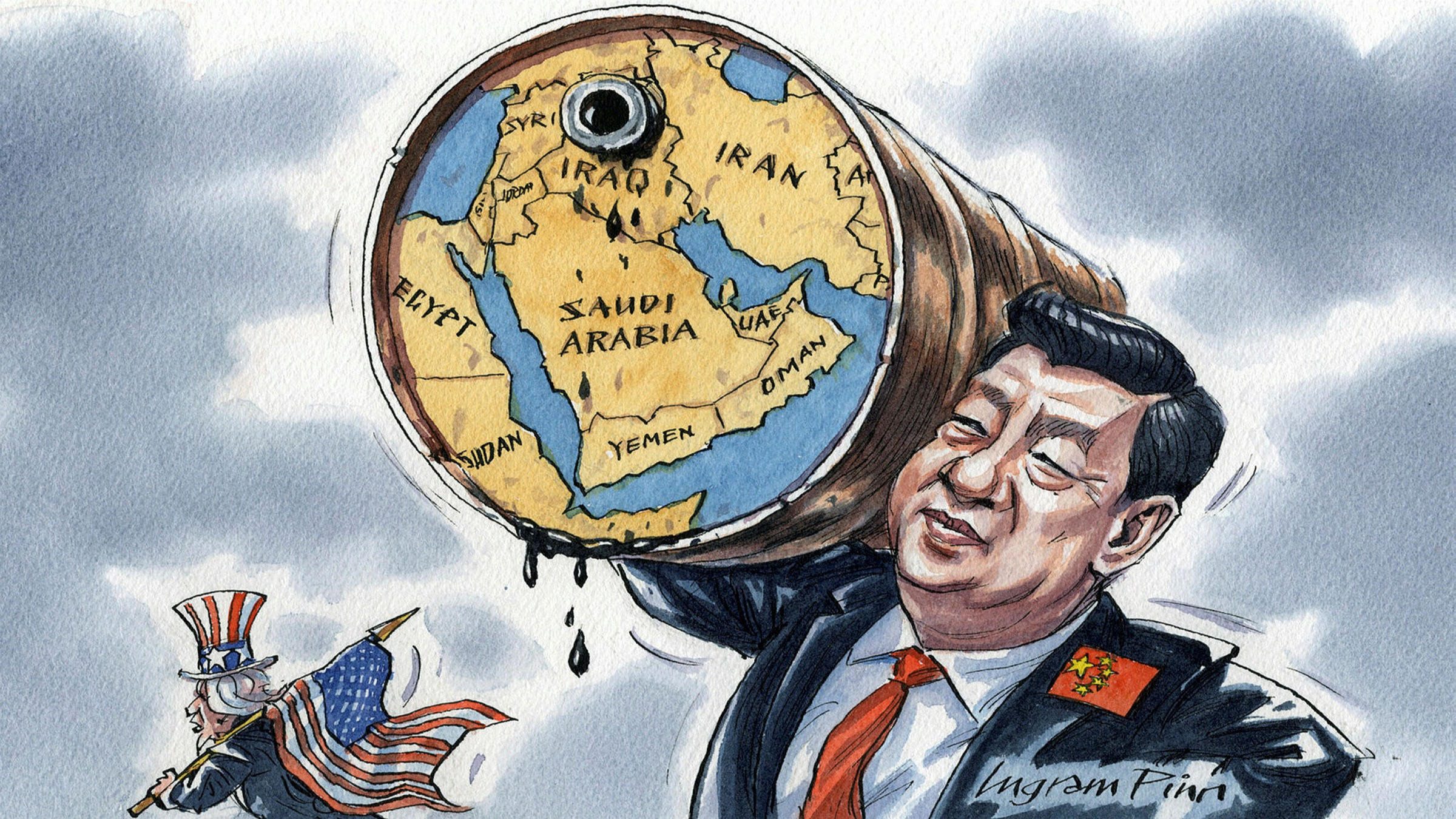
On Friday, March 10, China brokered a deal between Saudi Arabia and Iran, two countries that have been feuding for seven years over the violence that broke out at the Saudi embassy in Tehran. This deal formally restores all diplomatic relations between the two countries, reinstates security accords, revives trade agreements, and resumes investments. The countries released a joint statement iterating their “respect for the sovereignty of states and non-interference in internal affairs of states.”
This agreement gives hope for further cooperation and peace within the Middle East in the coming years. The aim for this deal is to influence other surrounding territories to increase engagement in security and stability within their respective countries. Many, however, have questioned what China’s role in all of this is and why they have a stake in the Middle East. The answer stems from oil within the region, which China relies on heavily.
China has been allowed to play this role due to the countries’ continuous oil trade with both Saudi Arabia and Iran despite the US’s sanctions on both countries. China remains a large purchaser of oil from Saudi Arabia, and Xi Jinping traveled to the country in December of 2022 to visit the crowned prince. China’s success in the Middle East has been connected to the countries’ “noninterference principle” according to Yu Jie, a senior research fellow for Chatham House, a think tank based in London. This principle means that China does not typically meddle in other countries’ internal affairs.
Why Does This Matter?
This recent turn of events begs the question: why is China so unforeseeably interested in the Middle East, and does this go beyond oil? Although claims relating to oil trade have been China’s primary reasoning for interfering in the Middle East, it doesn’t necessarily explain why the country is mending diplomatic relations and why they have waited until now to make this move directly after the US retreated from the Middle East.
The sudden interest also begs the question of whether China could be utilizing or manipulating the Middle East’s resources and people just as the US has done in the past. Although it is unclear what China’s true intentions are, it worries many countries that China may be trying to extend its reach to consolidate power worldwide.
Either way, if China is meddling in the Middle East, it could leave the countries in that region worse off than they already are. This is precisely what the US did when they intervened in Middle Eastern conflicts for years, then pulled out of the region suddenly, leaving it with no plan or government setup. This was disastrous for the area, leaving it in complete violence and chaos.
If China is seeking allies from Middle Eastern countries, or groups operating in the Middle East, this could pose a serious threat to other countries, mainly the US, and potentially incite war. Although as of yet, China has not explicitly shown any sort of interest in the politics of Middle Eastern countries. It would not be a far jump for the country to have some sort of influence over the region or eventually become heavily intertwined with Middle Eastern politics.
Some experts from the European Council on Foreign Relations seem to think that China will not play a part in security or politics within the Middle East for a while and that the country is more focused on trade within the region. Another topic these experts have cited as a reason for China’s sudden entrance into the Middle East is the Belt and Road Initiative, which involves significant global infrastructure investment that the country has been working on for years. For China, the Middle East is gravely important since the region connects to Africa and Europe, which would essentially complete the initiative.
China’s Other Recent Concerning Moves
On top of China’s recent moves in the Middle East, the country has also been making other international moves that have alarmed onlookers in the United States. These moves include maintaining relations with Russia throughout the Russo-Ukrainian War despite most other countries expelling Russian diplomats and removing their own diplomats from Russia, enforcing strong sanctions on Russia, and essentially excommunicating the country. This is concerning because it has the potential to show China is not necessarily as against the war as the rest of the world. At the very least, China is unwilling to stand in unison against unwarranted violence against other countries, which raises serious ethical issues from an international standpoint.
China is also in communication with North Korea, an isolationist country that most other countries have not easily been able to work with. China is North Korea’s biggest, and only, major trading partner. At the very least, this puts China in a position of soft power over North Korea, a country possessing the world’s largest military arsenal. With China whispering in the ear of North Korea, this could prove to be an eventually dangerous combination for the world.
The Chinese-operated balloons that entered American airspace not too long ago are also a major concern for the US. Although it is still unclear what the Chinese-operated balloon was doing over American airspace, the country has claimed the balloon was a weather tracking device. Contrary to this, US officials have claimed the device was doing much more than tracking weather patterns. China fired back at the US claiming that the US has flown at least ten spy balloons over Chinese airspace since January of 2022 without the country’s consent. The US National Security Council has publicly denied this allegation numerous times. This is another example of the nerve-wracking and unanticipated increase in unusual activity from China on an international level which gives the global community a reason to believe that the country may be up to something more.
What this Could Mean for the Rest of the World
China’s growing influence over these territories is concerning for many other parts of the world, especially the West. If China is looking to gain power, is it plausible that the country could be looking to build an alliance with these regions for the sake of warfare? It seems, based on the unpredictability of the countries’ motives, that it is completely plausible for other countries to assume the worst.
With the massive North Korean army, terrorist groups in the Middle East, and Russia’s nuclear arsenal, if China gained a strong alliance with these countries, President Xi Jinping would have all the makings for an all-out global war on the US and its allies. On top of this, China could pick and choose when and where to do this with a list of demands and warheads at the ready.
Several strategists have speculated about the possibility of imminent military action. Ross Babbage, a career strategic analyst writing for the New York Times, has claimed that a war with China is more imminent now than ever, outlining how he believes the country would execute this. Matthew Kroenig, vice president and senior director of the Atlantic Council’s Scowcroft Center for Strategy and Security as well as a columnist at Foreign Policy, posed the question of how the US can face two intertwined autocratic, revisionist countries with major nuclear arsenals. In addition to this, US General Mike Minihan, who heads the Air Force’s Air Mobility Command in Illinois, predicts that the war between China and US will begin by 2025.
China may also be trying to spread ideas from its own political regime and persuade other countries to shift over and follow in China’s footsteps: a sort of Eastern political influence in comparison to the immense Western influence that has presided over the world for decades. Western political ideology has found its way into many countries, influencing culture, religion, philosophy, technology, and more over many decades. Most importantly, the world has felt the heavy push for democracy from the West, which has at times polarized China with its more communist set of ideologies. It seems possible that China could be making an effort to spread its own ideological footprint over these Middle Eastern countries with the end goal of combatting some of the Western democratic ideas planted within the world. The benefit of this prospect for China is ultimately having more power and persuasion over the countries they can get to fall in line with communist ideals or those that may already oppose Western influences.
Another potential outcome of these moves could be that China is attempting to become more internationally involved and take on the position that the US currently holds, of a world mediator. This is a conclusion that China has already attempted to perpetuate internationally, denying any ulterior motives within the region. Regardless of what China’s true end goal is with these recent, strategic moves, it is clear that the world has its eyes on China and will be watching closely to see the outcome of future events unfold.
Featured Image Source: Financial Times





Comments are closed.